About us
FASTPCBA Co.,Ltd
-
 Building 1, Senyang Electronic Technology Park, Guangming High-tech Park, Yutang Street, Guangming District, Shenzhen City.
Building 1, Senyang Electronic Technology Park, Guangming High-tech Park, Yutang Street, Guangming District, Shenzhen City.
-
 F:86-13418481618
F:86-13418481618
-
 pcba13@fastpcba.cn
pcba13@fastpcba.cn
 date:2019-07-16 14:28:44
date:2019-07-16 14:28:44
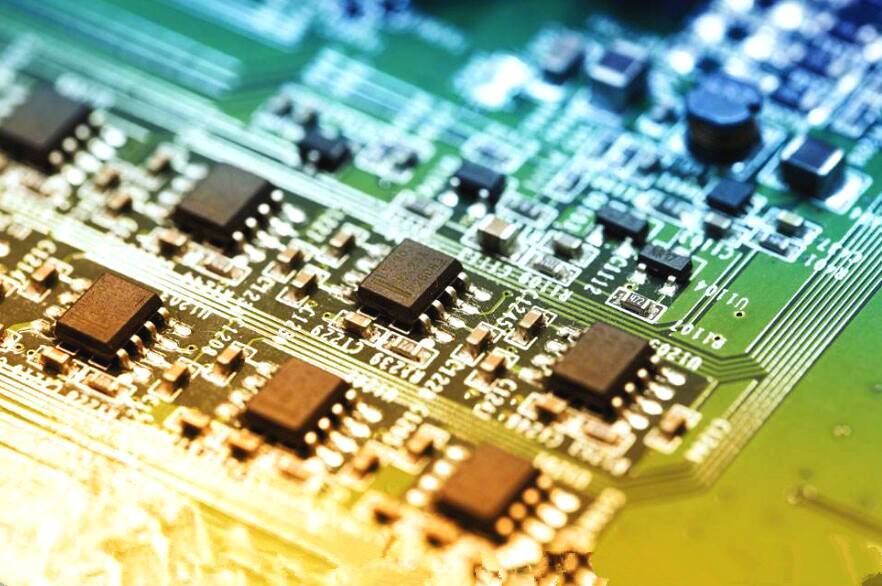
Various inspection standards ensure turnkey pcb manufacturing quality
When performing electronic processing at SMT Electronics Factory, QC will
execute quality inspection after the completion of turnkey pcb manufacturing. Due to many years of quality inspection experience, inspectors generally can quickly verify the PCBA board problem. The following are the turnkey pcb manufacturing processing appearance standards summarized by the professional quality inspectors of SMT processing plants through years of processing experience.
1. Weld point contact angle the angle between the poor fillet weld and the pad pattern joint is greater than 90°.
2. Upright: One end of the component leaves the pad and is tilted upright or upright.
3. Short circuit: The solder is connected between two or more solder joints that should not be connected, or the solder of the solder joint is connected to an adjacent conductor.
4. Empty welding: the component lead and the PCB solder joint are not connected by solder.
5. False soldering: The component leads and PCB solder joints seem to be connected, but they are not actually connected.
6. Cold welding: The solder paste at the solder joint is not completely melted or a metal alloy is not formed.
7. Less tin (insufficient tin): The area or height of the component end and PAD does not meet the requirements.
8. Multi-tin (too much tin): The area of the component and the PAD eat tin or the height exceeds the requirements.
9. Black solder joints: solder joints are black and dull.
10. Oxidation: Surfaces such as components, circuits, PADs or solder joints have chemical reactions and colored oxides.
11. Shift: the component is laterally (horizontal), longitudinal (vertical) or rotated in a plane offset from the predetermined position
12. Polarity (reverse): The direction or polarity of a component with polarity is inconsistent with the requirements of the file (BOM, ECN, component position map, etc.).
13. Floating height: There is a gap or height between the component and the PCB.
14. Wrong parts: Component specifications, models, parameters, shapes and other requirements do not match (BOM, samples, customer data, etc.).
15. Tin tip: The solder joints of the components are not smooth and the solder projection exist.
16. Multiple pieces: According to BOM and ECN or sample, etc., there should be no more parts in the position of the parts or redundant parts on the PCB.
17. Missing parts: According to the BOM and ECN or the sample, etc., the position of the parts to be attached or the parts of the PCB and the parts are not mounted.
18. Misalignment: The position of the component or component feet are moved to the position of other PAD or foot.
19. Open circuit (open circuit): PCB line disconnection phenomenon.
20. Side-displacement (side-standing): The sheet-shape elements with different widths and heights are placed sideways.
21. Reverse white (turning surface): The components have different symmetrical relative two-face interchangeable positions ,the chip resistor is common.
22. Tin beads: Small tin points between the components or between the PAD.
23. Bubbles: There are air bubbles inside the solder joints, components or PCB.
24.Climbing Tin: The solder joint height of the component solder joints exceeds the required height.
25. Tin crack: The solder joint has a cracked condition.
26. Hole plug: PCB plug hole or via hole is soldered or other blocked.
27. Damage: components, board bottom, board surface, copper foil, wiring, through holes, etc.,with cracking or cutting or damage phenomenon.
28. Silk screen blurring: The text or silk screen of components or PCBs is blurred or unscrewed and cannot be recognized or blurred.
29. Dirty: The board surface is unclean, and there are foreign objects or stains.
30. Scratch: Scratches such as PCB or buttons and bare copper foil.
31. Deformation: The component or PCB body or corners are not in the same plane or curved.
32. Foaming (layering) The PCB or component is layered with copper and platinum with a gap.
33. Overfill (excess glue) (excessive amount of red glue) or spillage requirements range.
34. Less glue (less red glue) or does not meet the required range.
35. Pinhole (pit): There are pinhole pits on PCB, PAD, solder joints, etc.
36. Burr (Pin): The edge or burr of the PCB is over the required range or length.
37. Gold finger impurities: There are abnormalities such as pitting, tin spots or anti-welding oil on the surface of the gold finger plating.
38. Gold finger scratch: The surface of the gold finger coating has scratched or exposed copper and platinum.
Above, I hope to help the manufacturers of turnkey pcb manufacturing plants, but the specific situation needs specific analysis. It can be combined with the above to achieve a faster quality inspection of the PCBA board.
 Building 1, Senyang Electronic Technology Park, Guangming High-tech Park, Yutang Street, Guangming District, Shenzhen City.
Building 1, Senyang Electronic Technology Park, Guangming High-tech Park, Yutang Street, Guangming District, Shenzhen City.
 F:86-13418481618
F:86-13418481618
 pcba13@fastpcba.cn
pcba13@fastpcba.cn